The Best Exercises for Hamstrings and How to Train Them Effectively
The hamstrings play a crucial role in athletic performance, injury prevention, and overall leg strength.
Whether you’re an athlete, a fitness enthusiast, or simply looking to strengthen your lower body, understanding how to train your hamstrings effectively can help you build muscle, enhance flexibility, and reduce the risk of injuries.
We’ll explore the best exercises for hamstrings, whether they respond better to high or low reps, the effects of cycling on hamstring development, and the balance between quadriceps and hamstring strength.
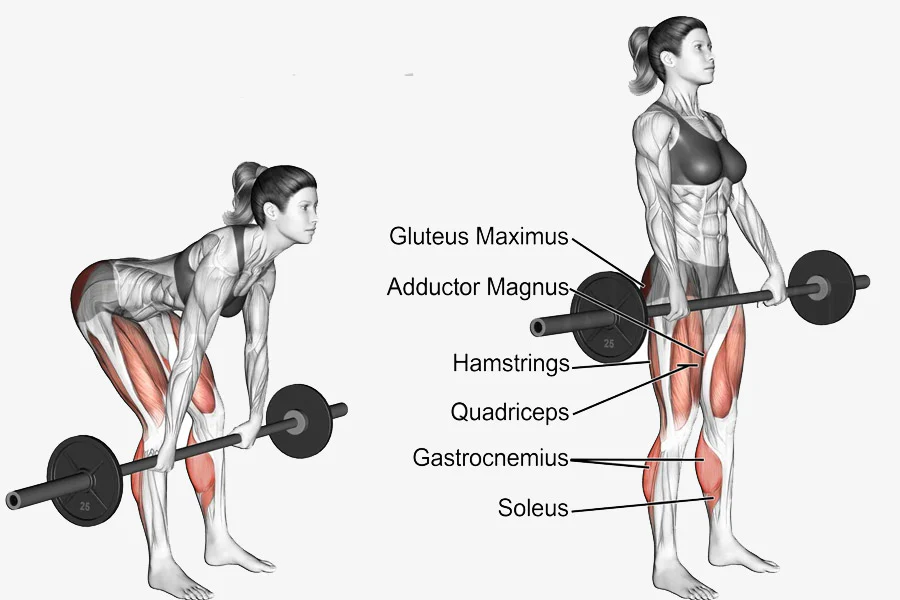
Best Exercises for Hamstrings
The hamstrings are composed of three muscles: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus.
They function primarily to extend the hip and flex the knee. Effective hamstring training should incorporate exercises that emphasize both of these functions. Here are some of the best exercises for targeting the hamstrings:
Romanian Deadlift (RDL)
Why it works: The Romanian deadlift is one of the best exercises for building hamstring strength and muscle mass. It primarily focuses on the hip hinge movement, placing significant tension on the hamstrings throughout the range of motion. How to do it:
- Stand with feet hip-width apart, holding a barbell or dumbbells in front of your thighs.
- Hinge at the hips, lowering the weight while keeping your back straight.
- Lower until you feel a strong stretch in your hamstrings, then return to the starting position.
Nordic Hamstring Curl
Why it works: This is a bodyweight exercise that emphasizes eccentric (lengthening) control of the hamstrings, which is highly effective for injury prevention and strength gains. How to do it:
- Kneel on a pad with your feet anchored (by a partner or machine).
- Slowly lower your torso toward the ground while maintaining control.
- Use your hamstrings to resist the descent and push back up.
Glute-Ham Raise
Why it works: This exercise isolates the hamstrings and provides an intense contraction throughout the movement. How to do it:
- Secure your feet in a glute-ham developer (GHD) machine.
- Lower your body forward while keeping a straight back.
- Engage your hamstrings to lift your torso back to the starting position.
Lying Leg Curl
Why it works: This machine exercise isolates the hamstrings, allowing you to focus on knee flexion without engaging other muscle groups. How to do it:
- Lie face down on the leg curl machine and position your ankles under the pad.
- Curl your legs up toward your glutes, squeezing at the top.
- Slowly lower back down to the starting position.
Single-Leg Romanian Deadlift
Why it works: This unilateral exercise helps correct imbalances and improves hamstring mobility and stability. How to do it:
- Hold a dumbbell in one hand while standing on the opposite leg.
- Hinge at the hips, lowering the weight while keeping your back straight.
- Return to the starting position and repeat.
Good Mornings
Why it works: A great hip-hinge movement that heavily engages the hamstrings while also strengthening the lower back. How to do it:
- Place a barbell on your upper back and stand with feet shoulder-width apart.
- Hinge at the hips, lowering your torso while keeping your spine neutral.
- Return to the standing position using your hamstrings and glutes.
Do Hamstrings Respond Better to High or Low Reps?
Hamstrings can benefit from both high and low reps, depending on the goal:
For strength and power: Lower reps (4-6) with heavier weights are effective for building maximal strength.
For muscle hypertrophy: Moderate reps (6-12) help increase muscle size through controlled time under tension.
For endurance and injury prevention: Higher reps (12-20) with lighter weights can enhance muscular endurance and tendon health.
Because the hamstrings are composed of both fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscle fibers, a combination of different rep ranges will yield the best results.
Is Cycling Good for Hamstrings?
Cycling is often associated with quad development, but it also engages the hamstrings. However, the extent to which the hamstrings are activated depends on cycling style and intensity:
Outdoor cycling: Engages the hamstrings more actively when climbing or pushing hard against resistance.
Indoor cycling (spinning): Primarily works the quads, but increasing resistance and focusing on the pull phase can activate the hamstrings.
Sprinting on a bike: Utilizes more hamstring engagement than steady-state cycling.
While cycling can help with hamstring endurance, it should not replace direct hamstring strengthening exercises.
Is It Better to Have Stronger Quads or Hamstrings?
A balanced strength ratio between the quadriceps and hamstrings is essential for overall leg function and injury prevention.
An imbalance can lead to issues such as ACL injuries, poor posture, and reduced athletic performance.
Stronger quads than hamstrings: This imbalance is common and can lead to knee instability, increasing the risk of ACL injuries.
Stronger hamstrings than quads: This is rare but could cause hip or lower back issues.
Ideal ratio: A balanced hamstring-to-quad strength ratio should be around 3:2, meaning your hamstrings should be about 70% as strong as your quads.
Training the hamstrings effectively involves a combination of hip-hinge and knee-flexion movements. Exercises such as Romanian deadlifts, Nordic hamstring curls, and glute-ham raises should be staples in your routine.
Hamstrings respond well to both low and high reps, depending on the training goal. While cycling can help with hamstring endurance, it should not replace targeted strength training.
Lastly, maintaining a balanced strength ratio between the hamstrings and quadriceps is crucial for injury prevention and optimal performance.
Prioritize hamstring training, and you’ll see improvements in athletic ability, strength, and overall lower-body development.





