The Best Macros for Building Muscle
Building muscle isn’t just about lifting heavy weights—it also requires proper nutrition, particularly the right balance of macronutrients. Macros, which consist of protein, carbohydrates, and fats, provide the fuel your body needs to grow and recover.
Understanding how to balance these nutrients effectively will help you maximize muscle growth, strength, and performance.
We’ll cover the best macronutrient ratio for muscle gain, how to calculate your macros, and which macros to prioritize throughout the day.
Understanding Macronutrients for Muscle Growth
To build muscle efficiently, you need a combination of three essential macronutrients:
- Protein: The building block of muscle, responsible for repairing and growing muscle fibers.
- Carbohydrates: The primary energy source that fuels your workouts and supports muscle recovery.
- Fats: Essential for hormone production, including testosterone, which plays a crucial role in muscle building.
While each macronutrient has its role, the key is to maintain the right balance so your body has everything it needs to grow effectively.
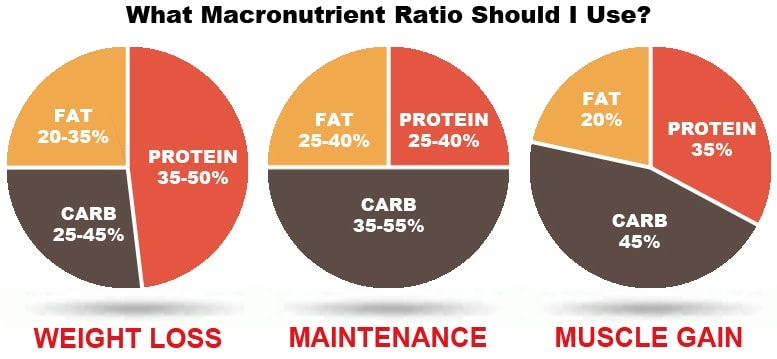
The Best Macronutrient Ratio for Building Muscle
While individual needs may vary based on factors like age, gender, metabolism, and training intensity, a common macronutrient ratio for muscle gain is:
- 40–50% carbohydrates
- 25–35% protein
- 15–25% fats
For example, if you are consuming 3,000 calories per day to support muscle growth, your macronutrient breakdown might look like this:
- Carbohydrates: 1,200–1,500 calories (300–375g)
- Protein: 750–1,050 calories (188–263g)
- Fats: 450–750 calories (50–83g)
This ratio ensures that you get enough protein for muscle repair while consuming enough carbs to fuel your workouts and enough fats to maintain hormonal balance.
Best Macros for Females
Women often have slightly different macronutrient needs due to hormonal differences and body composition. A recommended macronutrient breakdown for females aiming to build muscle is:
- 35–45% carbohydrates
- 30–35% protein
- 20–25% fats
For a woman consuming 2,500 calories per day for muscle gain, the breakdown might look like this:
- Carbohydrates: 875–1,125 calories (219–281g)
- Protein: 750–875 calories (188–219g)
- Fats: 500–625 calories (56–69g)
This slight variation accounts for different energy utilization and hormonal influences on muscle growth.

How to Calculate Your Macros for Muscle Gain
- Determine Your Caloric Needs
- Your total daily calorie intake should be in a slight surplus (250–500 calories above maintenance) to support muscle growth.
- Use an online calculator or the Harris-Benedict equation to estimate your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) and add extra calories based on your goal.
- Set Your Protein Intake
- Aim for 1.0–1.2 grams per pound of body weight.
- If you weigh 180 pounds, you should consume 180–216g of protein per day.
- Set Your Fat Intake
- Consume 0.3–0.4 grams per pound of body weight.
- For a 180-pound person, this equates to 54–72g of fat per day.
- Fill in the Rest with Carbohydrates
- Once protein and fat are calculated, the remaining calories should come from carbohydrates.
- Since 1g of protein = 4 calories and 1g of fat = 9 calories, you can determine your remaining calorie allowance and divide by 4 to get your carb intake.
Which Macros Should You Eat First?
Prioritizing the right macros at the right time can significantly impact your muscle-building progress. Here’s how to structure your intake throughout the day:
Pre-Workout (Carbs & Protein): Consume a meal rich in complex carbohydrates and lean protein about 60–90 minutes before your workout to fuel performance. Good options include chicken with rice, oatmeal with protein powder, or a banana with Greek yogurt.
Post-Workout (Protein & Fast-Digesting Carbs): After training, focus on consuming a high-protein meal with fast-digesting carbohydrates to replenish glycogen and kickstart muscle recovery. A protein shake with a banana or a lean chicken and rice meal is ideal.
Morning (Balanced Macros): Breakfast should include a mix of protein, healthy fats, and carbohydrates to stabilize energy levels throughout the day. Eggs with whole-grain toast and avocado or a protein smoothie with nuts and fruit are excellent choices.
Evening (Protein & Healthy Fats): Before bed, consuming slow-digesting protein such as casein (found in cottage cheese or Greek yogurt) along with healthy fats like almonds can help with overnight muscle recovery.
Additional Tips for Maximizing Muscle Growth
- Track Your Macros: Use a food tracking app to ensure you’re consistently hitting your targets.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration supports nutrient absorption and muscle function.
- Adjust as Needed: If you’re not gaining muscle, slightly increase your calorie intake.
- Be Patient: Muscle growth takes time—stay consistent with your nutrition and training.
Final Thoughts
Building muscle effectively requires more than just lifting weights—it demands a strategic approach to nutrition.
By understanding the best macronutrient ratios, calculating your macros accurately, and prioritizing the right nutrients at the right time, you can optimize your muscle-building journey.
Stick to your plan, monitor your progress, and adjust as needed to ensure steady and sustainable gains.